Tech & Wi-Fi
Nautical Wi-Fi Explained: Reliable Internet at Sea
Nautical Wi-Fi delivers fast, stable internet at sea using satellite networks. Learn about Starlink, hardware setup, costs, and best practices onboard.
01 February 2026
Nautical Wi-Fi Explained: Reliable Internet at Sea
Losing video calls or waiting endlessly for a file to upload can turn a Mediterranean cruise into a frustrating experience for remote workers and digital entertainment lovers alike. Staying productive or simply enjoying streaming services at sea now depends on more than luck, as nautical Wi-Fi technology blends satellite and terrestrial networks to deliver reliable, high-speed internet far from shore. This guide explains how modern cruise ships overcome maritime challenges to provide you with the seamless online experience you expect, whether docked in Greece or crossing open water.
Table of Contents
- What Is Nautical Wi-Fi Technology?
- Satellite Networks Versus Traditional Options
- How Cruise Ship Internet Works Onboard
- Key Hardware And Installation Requirements
- Pricing, Data Usage, And Practical Limitations
- Common Issues And How To Minimize Interruptions
Key Takeaways
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Nautical Wi-Fi Technology | Maritime Wi-Fi systems utilize satellite networks and advanced antenna systems to ensure reliable internet access in challenging environments. |
| Satellite vs. Traditional Networks | Satellite networks provide global coverage, while traditional options are limited to coastal areas; a hybrid approach can optimize performance. |
| Onboard Connectivity Challenges | Internet access at sea may be impacted by bandwidth limitations and environmental factors; passengers should prepare accordingly. |
| Pricing Models | Maritime internet pricing varies significantly from land services; understanding package types and data usage is crucial for cost management. |
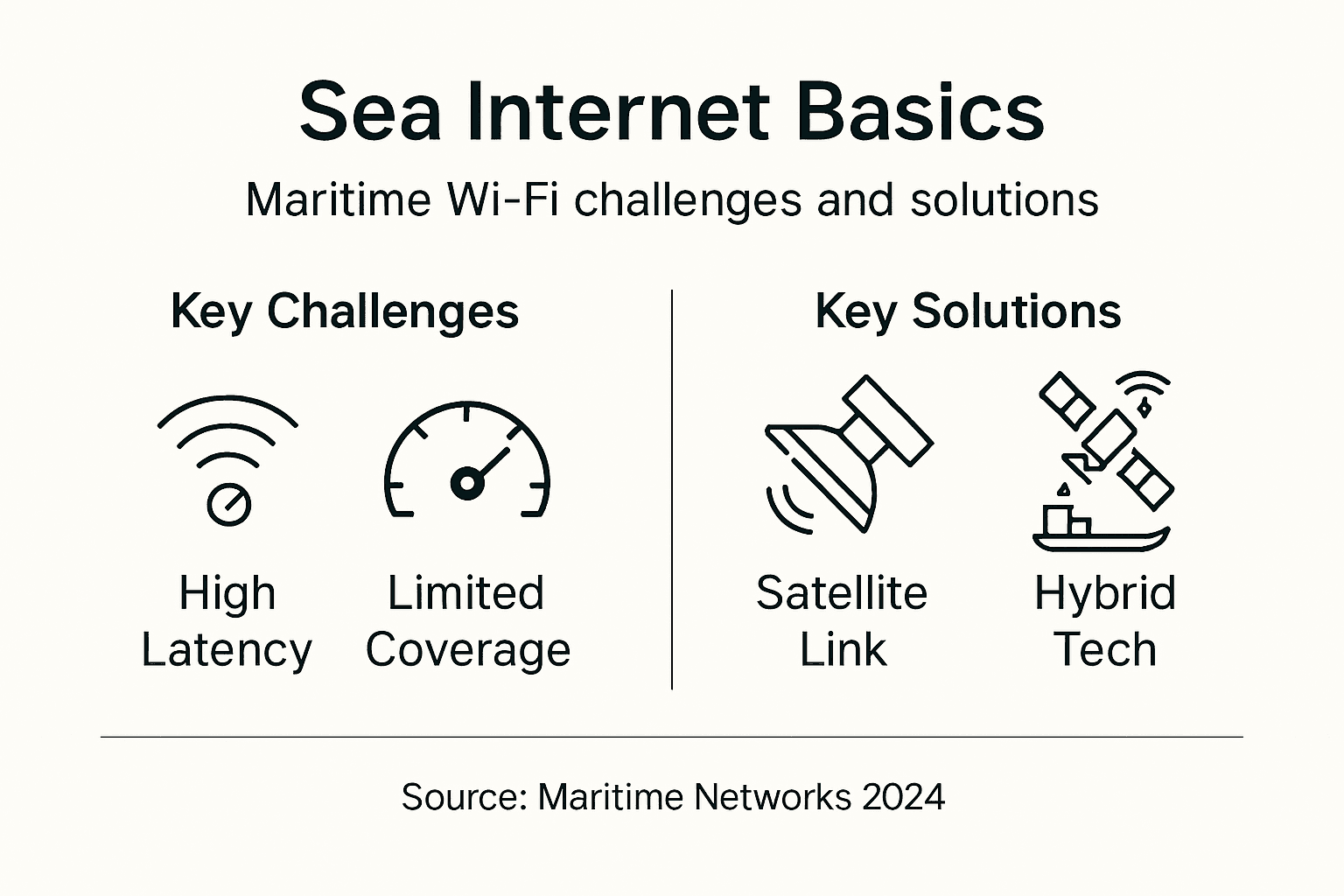
What Is Nautical Wi-Fi Technology?
Nautical Wi-Fi technology represents a sophisticated wireless communication system designed specifically for maritime environments. Unlike traditional land-based internet connections, these systems must overcome complex technical challenges to deliver reliable connectivity across vast oceanic regions. Maritime wireless communication networks integrate multiple technologies to ensure seamless internet access for passengers and crew.
The core of nautical Wi-Fi technology involves creating robust wireless networks that can function effectively in challenging marine conditions. These systems typically rely on a combination of technologies:
- Satellite Networks: Primary connectivity method providing wide-area coverage
- Cellular Signal Boosters: Enhancing signals near coastal regions
- Advanced Antenna Systems: Enabling signal reception in dynamic maritime environments
- Specialized Transmission Protocols: Optimizing data transfer across unpredictable connections
Modern nautical Wi-Fi implementations leverage cutting-edge technologies like Wi-Fi 6 and emerging spectrum technologies to deliver high-speed, low-latency internet experiences. These advancements mean travelers can now stream videos, conduct video conferences, and maintain continuous digital connectivity while traversing open waters.
Pro tip: Always verify your maritime internet package’s specific coverage and bandwidth capabilities before embarking on your sea journey.
Satellite Networks Versus Traditional Options
In the evolving landscape of maritime communications, comparing satellite networks with traditional connectivity options reveals a complex technological ecosystem. Satellite networks and conventional maritime communication methods each bring unique advantages and limitations to the table, creating a nuanced approach to maritime internet connectivity.
Traditional maritime communication technologies typically include:
- VHF Radio Systems: Short-range communication for vessel-to-vessel interactions
- 4G/5G Cellular Networks: Limited coastal connectivity
- High-Frequency (HF) Radio: Longer-range communication with higher signal variability
- Terrestrial Wireless Networks: Restricted to proximity of land-based infrastructure
Satellite networks, by contrast, offer remarkable advantages in global coverage and data transmission capabilities. Maritime communication strategies now increasingly integrate satellite solutions to overcome traditional communication constraints. These advanced networks provide continuous connectivity across oceanic regions, enabling real-time data transmission, navigation tracking, and seamless internet access for passengers and crew.
Satellite networks represent the future of maritime communication, bridging connectivity gaps where traditional methods fall short.
The primary trade-offs between satellite and traditional networks involve bandwidth, latency, and operational costs. While satellite systems deliver comprehensive global coverage, they typically incur higher expenses and experience slightly increased signal delay compared to localized terrestrial networks. Modern maritime communication strategies thus focus on hybrid approaches, strategically combining satellite and traditional technologies to maximize reliability and performance.
Here’s how satellite networks and traditional maritime options compare for onboard connectivity:
| Aspect | Satellite Networks | Traditional Options |
|---|---|---|
| Coverage | Global, ocean-wide | Limited to coastal areas |
| Bandwidth Availability | Moderate to high | Variable, often low |
| Latency | Higher due to distance | Lower, but location-bound |
| Operational Cost | Expensive, premium rates | Generally less costly |
| Reliability | Robust, weather-dependent | Can be affected by terrain |
Pro tip: Consider multi-technology communication packages that blend satellite and terrestrial networks for optimal maritime connectivity.
How Cruise Ship Internet Works Onboard
Understanding internet connectivity at sea requires exploring the complex technological infrastructure that enables digital communication while traversing oceanic regions. Cruise ship internet systems represent a sophisticated network of technologies designed to deliver reliable connectivity in challenging maritime environments.
The core components of onboard internet infrastructure include:
- Satellite Communication Systems: Primary data transmission method
- Wireless Access Points: Distributed throughout the vessel
- Network Management Gateways: Controlling bandwidth and security
- Signal Amplification Equipment: Enhancing connectivity across different ship areas
Satellite Signal Transmission forms the backbone of maritime internet connectivity. These systems rely on orbiting satellites positioned approximately 22,000 miles above Earth, creating a complex communication pathway that enables passengers to browse, stream, and communicate while at sea. Onboard network security plays a critical role in managing these intricate communication channels, ensuring both passenger access and operational protection.
Maritime internet connectivity represents a delicate balance between technological capability and operational constraints.
Passengers typically encounter internet access through metered packages that account for the high operational costs of satellite communication. Bandwidth limitations mean that while basic browsing and messaging are typically smooth, high-bandwidth activities like video streaming might experience reduced performance. Modern cruise lines are continuously improving their technological infrastructure to provide more robust and consistent internet experiences.
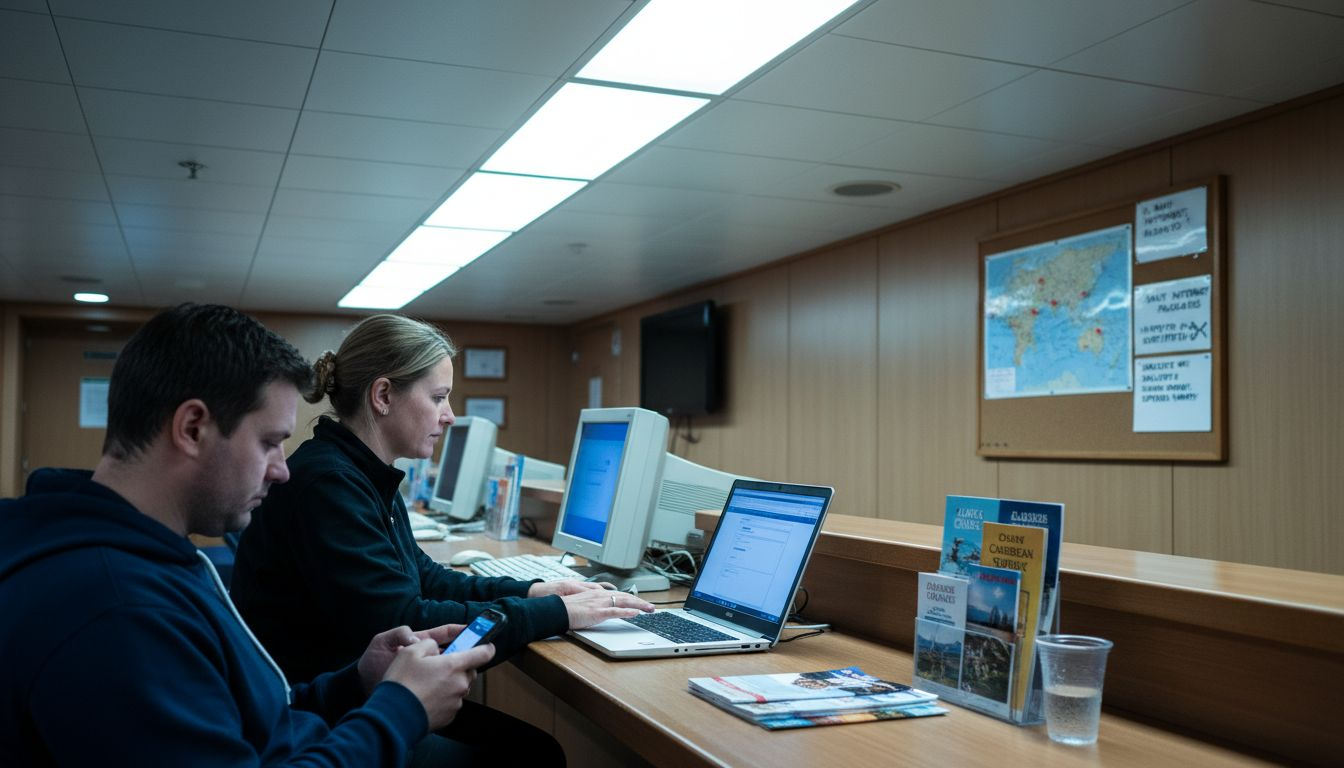

Pro tip: Purchase a comprehensive internet package and download essential content before sailing to maximize your onboard connectivity experience.
Key Hardware and Installation Requirements
Maritime Wi-Fi infrastructure demands specialized hardware meeting rigorous technical specifications. The unique maritime environment requires robust equipment capable of withstanding extreme conditions while maintaining consistent connectivity across challenging terrains.
Critical hardware components for nautical Wi-Fi include:
- High-Performance Access Points: Designed for marine environments
- Marine-Grade Satellite Terminals: Capable of sustained signal transmission
- Ruggedized Network Switches: Resistant to vibration and temperature variations
- Electromagnetic Interference Shielded Cables: Ensuring signal integrity
- Redundant Power Supply Systems: Maintaining continuous connectivity
Installation Requirements are equally complex. International Maritime Organization regulations mandate specific protocols for mounting and integrating communication equipment. These guidelines ensure that hardware can withstand maritime challenges such as constant motion, saltwater exposure, and extreme temperature fluctuations.
Maritime communication hardware must survive conditions that would disable standard terrestrial networking equipment.
Technical specifications for onboard Wi-Fi systems typically require multi-band support, enabling operations across 5 GHz and 6 GHz spectra. Advanced access points must provide seamless handoff between different signal zones, ensuring uninterrupted connectivity as passengers move throughout the vessel. Cybersecurity considerations also play a crucial role, with network design focusing on isolated operational zones and secure data transmission channels.
Pro tip: Always specify marine-certified networking equipment with proven durability ratings for maritime environments.
Pricing, Data Usage, and Practical Limitations
Maritime internet connectivity presents unique pricing challenges that significantly differ from traditional land-based internet services. Satellite transmission costs, specialized equipment, and operational complexities drive higher pricing structures that passengers must carefully navigate.
Typical maritime internet pricing models include:
- Time-Based Packages: Charging per minute of connectivity
- Data Volume Packages: Metered by gigabytes consumed
- Tiered Access Plans: Different speeds and usage limits
- Hybrid Packages: Combining time and data restrictions
- Per-Device Connection Fees: Additional charges for multiple device access
Bandwidth Limitations create substantial practical constraints for users. Wi-Fi connectivity trends demonstrate that maritime environments inherently restrict data transmission capabilities. Peak usage periods often result in significant network congestion, leading to throttled speeds and reduced performance for data-intensive applications like video streaming or large file transfers.
Maritime internet is a delicate balance between technological capability and economic constraints.
Environmental factors further complicate internet reliability, with weather conditions, vessel movement, and geographic location directly impacting signal quality. Satellite communication’s inherent latency means users experience slightly delayed connections compared to terrestrial networks. Network management strategies typically involve strict bandwidth controls to prevent excessive data consumption and maintain overall system performance.
Pro tip: Purchase a flexible internet package with rollover data and download critical content before your maritime journey.
Here is a summary of common internet pricing models and their best use scenarios at sea:
| Package Type | Best For | Data Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Time-Based | Short daily usage | Limited, fixed session times |
| Data Volume | Streaming or uploads | Metered, stops at data limit |
| Tiered Access | Group travel | Adjustable usage speeds |
| Hybrid | Mixed needs | Combines time and data limits |
| Per-Device Fee | Multi-device users | Pay per connected device |
Common Issues and How to Minimize Interruptions
Maritime internet connectivity presents unique challenges requiring strategic management. Internet interruption risks stem from complex environmental and technological factors that demand proactive mitigation strategies for consistent onboard communication.
Common connectivity interruption sources include:
- Atmospheric Interference: Signal disruption from weather conditions
- Physical Cable Damage: Potential breaks from maritime activities
- Satellite Signal Blockage: Obstructions affecting transmission
- Electromagnetic Interference: Equipment-related signal disruptions
- Geographic Coverage Limitations: Reduced signal strength in remote areas
Network Resilience requires comprehensive approaches. Submarine cable protection strategies emphasize multiple redundancy methods to ensure continuous connectivity. Advanced maritime networks now incorporate dynamic rerouting capabilities, allowing instant traffic redirection when primary communication channels experience interruptions.
Successful maritime internet relies on anticipating and rapidly responding to potential disruption scenarios.
Technical mitigation techniques involve implementing robust network architectures with multiple satellite and terrestrial communication pathways. Sophisticated monitoring systems continuously evaluate signal quality, automatically switching between available channels to maintain stable internet access. Cruise lines increasingly invest in advanced communication technologies that provide seamless backup mechanisms, ensuring passengers experience minimal service interruptions.
Pro tip: Always download critical offline content and have communication backup plans before embarking on maritime journeys.
Experience Seamless Internet with Seafy Onboard
The article highlights challenges such as limited bandwidth, high costs, and reliability issues inherent to maritime internet powered by satellite networks and complex hardware installations. If you want to avoid frustrating interruptions and slow connectivity while at sea, especially on cruise ships or ferries, you should consider a solution designed specifically for these unique conditions. Seafy understands these pain points and delivers reliable, high-speed Wi-Fi connectivity onboard vessels navigating the Mediterranean and beyond. By integrating advanced satellite technologies like Starlink and offering user-friendly internet packages through its digital platform, Seafy ensures passengers and crew stay connected for work, entertainment, and communication without compromise.
Ready to transform your maritime internet experience? Visit Seafy today to explore flexible Wi-Fi packages tailored for your journey. Discover how partnering with major ferry lines like Corsica Ferries and GNV helps provide stable connections even amid the challenges of satellite communication. Don’t settle for limited internet access at sea when you can enjoy consistent onboard connectivity through Seafy’s digital platform. Start your voyage with confidence and stay connected wherever the ocean takes you.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is nautical Wi-Fi technology?
Nautical Wi-Fi technology is a sophisticated wireless communication system designed for maritime environments, ensuring reliable internet connectivity across vast oceanic regions using satellite networks, cellular signal boosters, and advanced antennas.
How does internet connectivity work on cruise ships?
On cruise ships, internet connectivity is primarily facilitated through satellite communication systems, wireless access points, and network management gateways, allowing passengers to browse, stream, and communicate as the ship traverses the oceans.
What are the main differences between satellite networks and traditional maritime communication options?
Satellite networks provide global coverage and higher bandwidth but come with increased costs and latency, whereas traditional options like VHF radio and cellular networks are limited to coastal areas and offer variable bandwidth.
What factors affect the reliability of maritime internet connectivity?
Maritime internet reliability can be influenced by atmospheric interference, physical cable damage, satellite signal blockage, electromagnetic interference, and geographic coverage limitations, which can lead to potential interruptions in service.